Cold Holding Temperature Check Tool
Check The Cold Holding Temperature Of Your Desired Food Below!
Maintaining proper food temperatures is crucial for preventing bacterial growth and foodborne illnesses. When it comes to cold holding temperatures, understanding the safe limits is essential for food service establishments, grocery stores, and households.
This comprehensive guide delves into the maximum cold holding temperature, exploring its significance, regulations, and best practices.
What is Cold Holding Temperature
Cold holding temperature refers to the required temperature range at which potentially hazardous foods must be stored to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. These foods include:

- Meat, poultry, and seafood
- Dairy products
- Cooked plant-based foods
- Cut melons and other cut produce
- Cooked rice, pasta, and other grains
The Importance of Proper Cold Holding Temperatures
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USDA), bacteria that cause foodborne illnesses grow rapidly at temperatures between 40°F (4.4°C) and 140°F (60°C).
This range is known as the “Danger Zone.” Maintaining cold holding temperatures below 40°F (4.4°C) significantly slows down bacterial growth, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Cold Holding Temperature Regulations
Food safety regulations set by government agencies and industry organizations aim to ensure food is held at safe temperatures throughout the supply chain, from production to consumption.
Here are some notable regulations:
- FDA Food Code: Requires cold holding temperatures of 41°F (5°C) or below for potentially hazardous foods.
- USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service: Mandates cold holding temperatures of 40°F (4.4°C) or below for meat, poultry, and egg products.
- National Restaurant Association ServSafe: Recommends keeping cold foods at 41°F (5°C) or below.
Best Practices for Maintaining Safe Cold Holding Temperatures

Here are some best practices for maintaining safe cold holding temperatures for potentially hazardous foods:
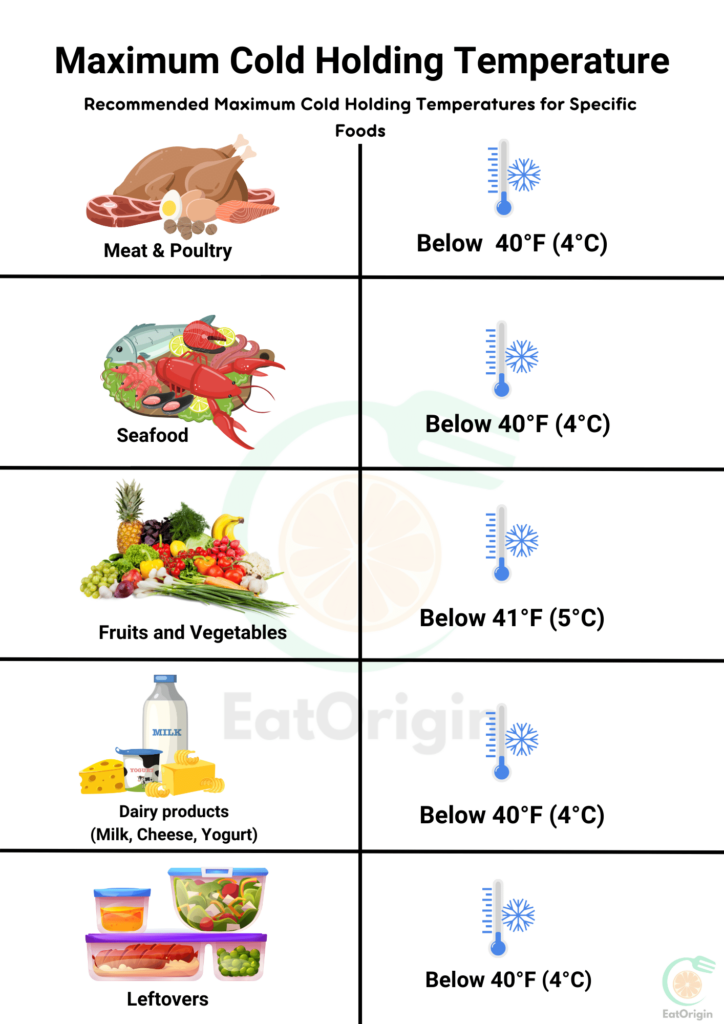
- Keep potentially hazardous foods at 40°F (4°C) or below. This temperature slows down the growth of most bacteria.
- Store cold foods in clean, properly functioning refrigerators or walk-in coolers. Make sure the units can maintain foods at the required temperature.
- Use a food-grade thermometer to regularly check the internal temperatures of foods. Log temperatures as part of your HACCP program.
- Allow enough space between foods and walls in refrigeration units for proper air circulation. Overstocking can lead to improper cooling.
- Cool cooked hot foods from 140°F to 70°F within 2 hours, and then from 70°F to 40°F or below within the next 4 hours, using shallow pans or an ice bath.
- Limit how often and how long refrigerator/freezer doors are open to maintain consistent cooling.
- Accept deliveries of cold foods only if they were transported and received at 40°F or below.
- Routinely check dates and discard expired refrigerated foods that may have been temperature abused.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and maintaining refrigeration units for optimal performance.
Maximum Cold Holding Temperature For Specific Food: The FDA Guideline
The FDA Food Code establishes the maximum cold holding temperature for potentially hazardous foods below 41°F (5°C). This temperature limit is widely adopted by state and local health departments across the United States.
According to the FDA:
“Potentially hazardous food shall be cooled to 41°F (5°C) or less within 4 hours if prepared from ingredients at ambient temperature, and to 41°F (5°C) or less within 4 hours, if removed from hot holding at 135°F (57°C) or higher.”
Highest temperature allowed for cold holding tuna salad
The maximum cold holding temperature allowed for tuna salad is 40°F (4°C) or below. Tuna salad contains potentially hazardous ingredients like mayonnaise,
which is a protein-rich food that can support the growth of harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria if not kept at proper temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for shredded lettuce
The cold holding temperature allowed for shredded lettuce is 41°F (5°C) or below. Once lettuce is cut or shredded,
it becomes potentially hazardous because the exposed internal surfaces provide a nutrient-rich environment where bacteria can grow if not kept at safe cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature for cut cantaloupe
The cold holding temperature for cut cantaloupe is 41°F (5°C) or below. Like other cut fruits,
cantaloupe becomes potentially hazardous after being cut because the exposed flesh can support the growth of harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria if not held at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for pasta salad
The cold holding temperature allowed for pasta salad is 41°F (5°C) or below. Pasta salad often contains ingredients like mayonnaise or eggs,
which are protein-rich and can support the growth of harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria if not kept at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for sliced fruit
The cold holding temperature allowed for sliced fruit is 41°F (5°C) or below. Once fruits are cut or sliced,
they become potentially hazardous because the exposed internal surfaces provide a nutrient-rich environment where bacteria can grow if not kept at safe cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for sliced egg salad sandwiches
The cold holding temperature allowed for sliced egg salad sandwiches is 41°F (5°C) or below. Egg salad sandwiches contain potentially hazardous ingredients like eggs and mayonnaise,
which are protein-rich and can support the growth of harmful bacteria like Salmonella if not kept at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for a green salad
The cold holding temperature allowed for a green salad is 41°F (5°C) or below. While fresh greens are not initially hazardous, once they are cut or processed,
they become potentially hazardous because the exposed internal surfaces provide a nutrient-rich environment where bacteria can grow if not kept at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature for fresh beef
The cold holding temperature for fresh beef is 40°F (4°C) or below. Raw meats like fresh beef are considered potentially hazardous because they can harbor harmful bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, which can multiply rapidly if not kept at safe cold temperatures.
Max temperature allowed while cold holding tomato salsa
The maximum temperature allowed while cold holding tomato salsa is 41°F (5°C) or below. Like other fresh salsas, tomato salsa can be potentially hazardous due to its ingredients like tomatoes, onions, and cilantro, which can support the growth of harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria if not kept at safe cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for cut vegetables
The cold holding temperature allowed for cut vegetables is 41°F (5°C) or below. Once vegetables are cut or processed,
they become potentially hazardous because the exposed internal surfaces provide a nutrient-rich environment where bacteria can grow if not kept at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature allowed for deli meat?
The cold holding temperature allowed for deli meat is 40°F (4°C) or below. Deli meats are considered potentially hazardous foods because they can harbor harmful bacteria like Listeria and Salmonella, which can multiply rapidly if not kept at proper cold temperatures.
Cold holding temperature for cut fruit
The cold holding temperature for cut fruit is 41°F (5°C) or below. Once fruits are cut or sliced, they become potentially hazardous because the exposed internal surfaces provide a nutrient-rich environment where bacteria can grow if not kept at safe cold temperatures.
Conclusion
Maintaining proper cold holding temperatures is a critical aspect of food safety and quality assurance. By adhering to the FDA’s recommended guidelines, food service establishments can ensure the safety of their customers and minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
This comprehensive article has provided valuable insights into the specific cold holding temperatures required for various types of foods, empowering readers to make informed decisions and implement best practices in their food handling and preparation processes.